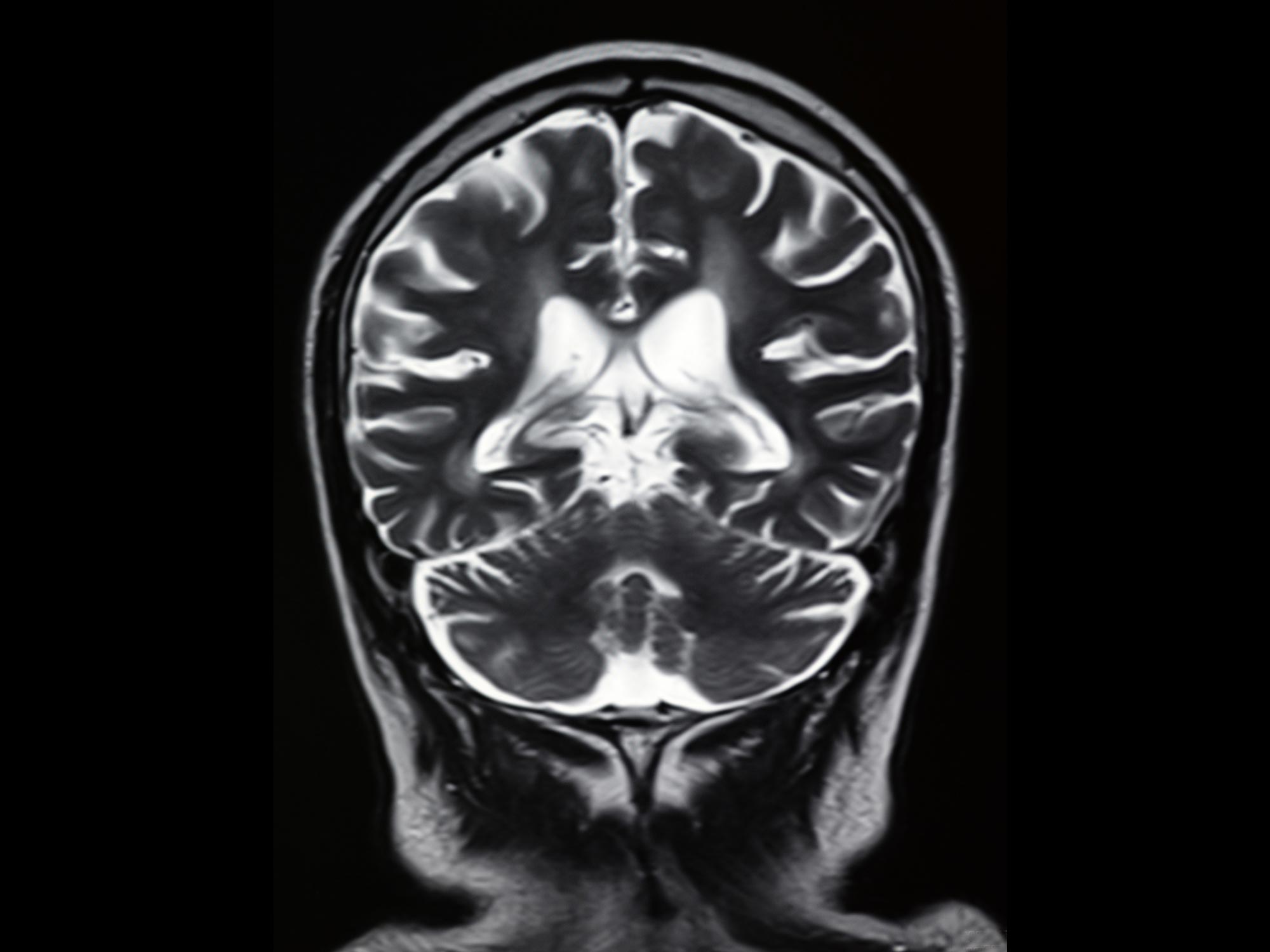
Nesen veiktais pētījums, ko vadīja Kalifornijas Universitātes Losandželosas pētnieki, atklāja, ka cilvēkiem, kuri ilgstoši dzīvo ar COVID un kuriem ir anosmija (ožas zudums), ir atšķirīgi smadzeņu darbības modeļi, salīdzinot ar tiem, kuri ir atguvuši ožu vai kuri nekad nav bijis COVID-19. Novērošanas pētījumā tika izmantota MRI skenēšana un tika atklāta samazināta smadzeņu aktivitāte un traucēta savienojamība starp orbitofrontālo garozu un prefrontālo garozu cilvēkiem ar ilgstošu COVID-19 anosmiju. Šī saikne netika ietekmēta tiem, kuri pēc COVID atguva ožu. Rezultāti liecina, ka ilgstošs COVID-19 ožas zudums var būt saistīts ar izmaiņām smadzenēs, kas neļauj pareizi apstrādāt smakas, taču, tā kā tas ir klīniski atgriezenisks, ožas trenēšana var palīdzēt smadzenēm atgūt šo sajūtu. Pētījumā arī konstatēts, ka cilvēku smadzenes ar ilgstošu COVID-19 smakas zudumu var kompensēt to, stiprinot savienojumus ar citām maņu zonām.
Jauns pētījums, ko vadīja Londonas Universitātes koledžas (UCL) pētnieki, atklāj, ka cilvēkiem, kuri ilgstoši dzīvo ar COVID un kuriem ir ožas zudums, konkrētos smadzeņu reģionos ir atšķirīgi darbības modeļi.
Pētījumā tika izmantota MRI skenēšana, lai salīdzinātu smadzeņu darbību cilvēkiem ar ilgstošu COVID, kuri bija zaudējuši ožas sajūtu, tiem, kuru smarža pēc inficēšanās ar COVID atgriezās normālā stāvoklī, un cilvēkiem, kuriem nekad nav bijis pozitīvs tests.[{” attribute=””>COVID-19.
Published in the journal eClinicalMedicine, the observational study found that people with long COVID smell loss had reduced brain activity and impaired communication between two parts of the brain that process important smell information: the orbitofrontal cortex and the pre-frontal cortex. This connection was not impaired in people who had regained their sense of smell after COVID.
The findings suggest smell loss, known as anosmia, caused by long COVID is linked to a change in the brain that stops smells from being processed properly. Because it’s clinically reversible, as shown in some subjects, it may be possible to retrain the brain to recover its sense of smell in people suffering the side effects of long COVID.
Dr. Jed Wingrove (UCL Department of Medicine) the lead author of the study, said: “Persistent loss of smell is just one way long COVID is still impacting people’s quality of life – smell is something we take for granted, but it guides us in lots of ways and is closely tied to our overall wellbeing. Our study gives reassurance that, for the majority of people whose sense of smell comes back, there are no permanent changes to brain activity.”
Joint senior author, Professor Claudia Wheeler-Kingshott (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology), said: “Our findings highlight the impact COVID-19 is having on brain function. They raise the intriguing possibility that olfactory training – that is, retraining the brain to process different scents – could help the brain to recover lost pathways, and help people with long COVID recover their sense of smell.”
Researchers say their findings also suggest that the brains of people with long COVID smell loss might be compensating for this lost sense by boosting connections with other sensory regions: their brains had increased activity between the parts of the brain that process smell and areas that process sight (the visual cortex).
“This tells us that the neurons that would normally process smell are still there, but they’re just working in a different way,” said Dr. Wingrove.
Professor Rachel Batterham (UCL Division of Medicine), also joint senior author of the study said: “This is the first study to our knowledge that looks at how brain activity changes in people with long COVID smell loss. It builds on the work we undertook during the first wave of the pandemic, which was one of the first to describe the link between COVID-19 infection with both loss of smell and taste.”
Reference: “Aberrant olfactory network functional connectivity in people with olfactory dysfunction following COVID-19 infection: an exploratory, observational study” by Jed Wingrove, Janine Makaronidis, Ferran Prados, Baris Kanber, Marios C. Yiannakas, Cormac Magee, Gloria Castellazzi, Louis Grandjean, Xavier Golay, Carmen Tur, Olga Ciccarelli, Egidio D’Angelo, Claudia A.M. Gandini Wheeler-Kingshott and Rachel L. Batterham, 2 March 2023, eClinicalMedicine.
DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101883
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR).